Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Gestational diabetes insipidus. treatment for most people with gestational diabetes insipidus is with the synthetic hormone desmopressin. primary polydipsia. there is no specific treatment for this form of diabetes insipidus, other than decreasing fluid intake. if the condition is related to a mental illness, treating the mental illness may. Diabetes insipidus is a condition that results from insufficient production of the antidiuretic hormone (adh), a hormone that helps the kidneys and body conserve the correct amount of water. normally, the antidiuretic hormone controls the kidneys' output of urine. it is secreted by the hypothalamus insipidus diabetes n (a small gland located at the base of the.
Diabetes insipidus niddk.
Signs and symptoms of diabetes insipidus include: 1. extreme thirst 2. producing large amounts of diluted urine 3. frequent need to get up to urinate during the night 4. preference for cold drinksif your condition is serious, urine output can be as much as 20 quarts (about 19 liters) a day if you're drinking a lot of fluids. a healthy adult typically urinates an average of 1 or 2 quarts (about 1 to 2 liters) a day. an infant or young child with diabetes insipidus may have the following signs a Diabetesinsipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.. there are four types of di, each with insipidus diabetes n a different set of causes. Diabetesinsipidus is a type of diabetes that results in large amounts of urine produced in the kidneys. the tests for diabetes insipidus diagnosing are fluid deprivation, urinalysis, mri and blood tests. these also prescribed by the doctor based on the types of diabetes insipidus.
Central Diabetes Insipidus Genetic And Rare Diseases
Diabetes insipidus occurs when your body can't properly balance the body's fluid levels. when your fluid regulation system is working properly, your kidneys help maintain this balance. the kidneys remove fluids from your bloodstream. this fluid waste is temporarily stored in your bladder as urine, until you urinate. the body can also rid itself of excess fluids through sweating, breathing or diarrhea. a hormone called anti-diuretic hormone (adh), or vasopressin, insipidus diabetes n helps control how fast or slow f With diabetes insipidus, “diabetes” means an increased passing of urine, and “insipidus” means tasteless; so diabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by the production of large quantities of dilute and tasteless urine. myasthenia gravis myelitis myeloma myeloproliferative disorders myopathy myositis n nail patella syndrome narcolepsy naturopathy necrotizing fasciitis nephrogenic diabetes insipidus neuroblastoma neurofibromatosis neurological diseases neutropenia niacin night terrors Covid-19 has changed the nature of medical consultations, emphasizing virtual patient counseling, with relevance for patients with diabetes insipidus (di) or hyponatraemia. the main complication of desmopressin treatment in di is dilutional hyponatraemia. since plasma sodium monitoring is not always.

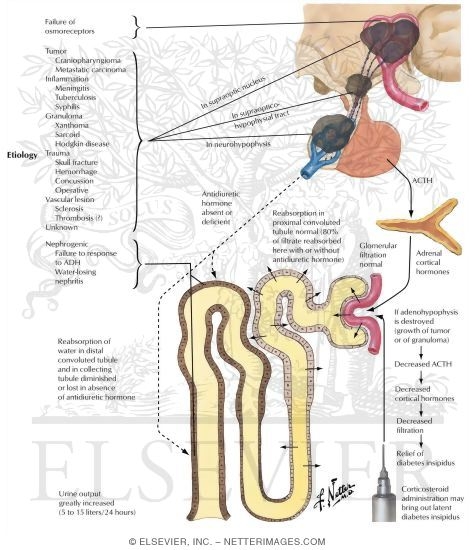
Central diabetes insipidus. if you have mild diabetes insipidus, you may only need to increase your water intake. if the condition is caused by an abnormality in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus (such as a tumor), your doctor will first treat the abnormality. Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition in which there is a problem with the secretion of antidiuretic hormone. patients with diabetes insipidus have high amounts of urine that is diluted (clear) because of this inability to control the amount of water in the urine. Some of the tests doctors use to diagnose diabetes insipidus include: 1. water deprivation test. while being monitored by a doctor and health care team, insipidus diabetes n you'll be asked to stop drinking fluids for several hours. to prevent dehydration while fluids are restricted, adh allows your kidneys to decrease the amount of fluid lost in the urine. while fluids are being withheld, your doctor will measure changes in your body weight, urine output, and the concentration of your urine and blood. your doctor

Traumatic brain insipidus diabetes n injury (tbi) is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in many age groups. neuroendocrine dysfunction has been recognized as a consequence of tbi and consists of both anterior and posterior pituitary insufficiency; water and electrolyte abnormalities (diabetes insipidus (di) and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (siadh are amongst the most. Central diabetes insipidus (di) is a form of di that occurs when the body has lower than normal levels of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin), which is characterized by frequent urination. diabetes insipidus is subdivided into central and nephrogenic di.. two other forms are gestational di and primary polydipsia (dipsogenic di). central di results from damage to the pituitary gland, which.
See full list on mayoclinic. org. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is a long name for an uncommon condition. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is not the same as diabetes mellitus. diabetes mellitus causes elevated blood sugar levels. Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day. Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day.
Diabetes insipidus, is a debilitating and rare disease, with a prevalence of 1 out of 25,000 people. often referred to as “water diabetes,” it is a condition characterized by frequent and heavy urination, excessive thirst and an overall feeling of weakness. If you have diabetes insipidus: 1. prevent dehydration. as long as you take your medication and have access to water when the medication's effects wear off, you'll prevent serious problems. plan ahead by carrying water with you wherever you go, and keep a supply of medication in your travel bag, at work or at school. 2. wear a medical alert bracelet or carry a medical alert card in your wallet. if you have a medical emergency, a health care professional will recognize immediately your need fo Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus that's present at or shortly after birth usually has an inherited (genetic) cause that permanently changes the kidneys' ability to concentrate the urine. nephrogenic diabetes insipidus usually affects males, though women can pass the gene on to their children.
Diabetes insipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.